Resources for Patients
Select a resource below to view, download, or print.
Starting the Toujeo Journey



Resources for Patients New to Toujeo

What to Understand:
A handy guide overviewing Toujeo, from efficacy and safety to coverage

Starting and Staying on Toujeo:
Information for patients starting Toujeo

How to Use Toujeo Pens Injection Guide:
A patient-friendly guide with information about Toujeo and how to use it

Diabetes Education

Learning More About Insulin:
An introduction to insulin and both T1DM and T2DM
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia Awareness:
Tips for patients about understanding hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia

Blood Sugar Log:
A form to track blood glucose levels throughout the week
Meal Planning and Exercise Tips:
Tips for keeping active to stay healthy
- Start Toujeo at the dose prescribed by your doctor
- After you start Toujeo, your doctor may adjust your insulin dose. Be sure to take Toujeo once a day at the same time
- Be sure to review the full Instructions for Use for Toujeo
- Toujeo is injected under your skin
- Rotate injection site within these regions from one injection to the next to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into affected areas
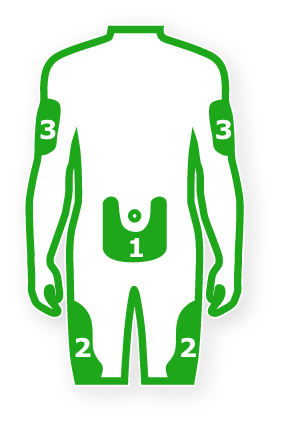

Stomach - Inject anywhere except for a 2-inch radius around navel.

Thighs - Avoid injecting too close to bony area above knee.

Upper arms - Inject into fatty tissue on outer back area of upper arm.
Your doctor may change your Toujeo dose several times in the first few weeks. This is to be expected. There are many reasons your doctor might increase your dose, and it’s a part of a process to help manage your blood sugar levels. If your dose increases, it doesn’t mean you’re doing anything wrong. Working together, you and your doctor will find the appropriate dose for you.
Remember: When you start on Toujeo, it could take at least 5 days for Toujeo to reach its full activity in patients with T1DM.1
Keep track of your blood sugar levels and your insulin dose, following the schedule worked out with your doctor. Download the free Blood Sugar Log to help you keep track.
For all insulins, including Toujeo, the most common side effect is hypoglycemia. Ask your doctor about the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, how to monitor your blood sugar, and what to do if you have a hypoglycemic event.1
Find out more about side effects here.


Resources for Providers
Select a resource below to view, download, or print.
Starting your patients on Toujeo


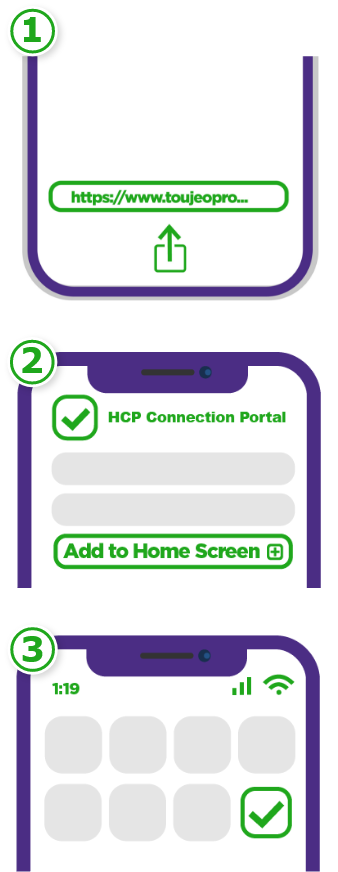
HCP Connection Portal—your one-stop support site for Sanofi insulin brand resources
Gain access to patient resources, samples, product information, and so much more. Visit the HCP Connection Portal to get started.

Want quick access to the HCP Connection Portal?
Add the HCP Connection Portal to your
home screen for
Apple iOS and Android
Publications

BRIGHT: The first head-to-head study of Toujeo vs Tresiba® in patients with T2DM

InRange: Comparing Toujeo vs Tresiba in adults with T1DM using time-in-range as the primary endpoint

Deliver G: Retrospective analysis of patients with T2DM receiving GLP-1 RA therapy

EDITION 1*: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using basal and mealtime insulin

EDITION 2*: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using oral antidiabetic agents and basal insulin

EDITION 3*: Insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on oral glucose-lowering drugs

EDITION 4*: Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus

BAILEY: A PK/PD study evaluating the within-day variability of Toujeo and Tresiba

Clamp Study 1: Evaluated the steady-state PK/PD profile of Toujeo

Clamp Study 2: Evaluated the day-to-day and intra-day variability of Toujeo
Toujeo has been studied versus Lantus® (insulin glargine injection) 100 Units/mL in 4 pivotal clinical trials (the EDITION study program)* involving more than 3000 patients and in 2 euglycemic clamp studies to assess PK and PD.1-3
*All studies in the EDITION clinical program were 26-week, open-label, controlled, titrate-to-target, noninferiority studies in adults with diabetes not at A1C goal (range: 7%-10% or 11%), randomized to Toujeo or Lantus once daily. All patients were titrated to an FPG goal of 80 to 130 mg/dL (T2DM) or 80 to 130 mg/dL (T1DM).1,4


Need help with access support?
Sanofi Patient Connection® can help your office obtain prior authorizations for Toujeo.

Order samples today†‡
Have samples delivered to your office.
†US-licensed prescribers are required to register to request samples.
Indication
Toujeo is a long-acting human insulin analog indicated to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older with diabetes mellitus. Limitations of Use: Toujeo is not recommended for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection
Important Safety Information
Contraindications
Toujeo is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to insulin glargine or any of the excipients in Toujeo.
Warnings and Precautions
Toujeo contains the same active ingredient, insulin glargine, as Lantus. The concentration of insulin glargine in Toujeo is 300 units per mL (U-300).
Insulin pens and needles must never be shared between patients. Do NOT reuse needles.
Monitor blood glucose in all patients treated with insulin. Modify insulin regimens only under medical supervision. Changes in insulin regimen, strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration may result in the need for a change in insulin dose or an adjustment in concomitant oral antidiabetic treatment. Changes in insulin regimen may result in hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Dosage adjustments are recommended to lower the risk of hypoglycemia when switching patients to Toujeo from another insulin therapy.
Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis may result in hyperglycemia; sudden change in the injection site (to unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia. Advise patients to rotate injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia.
Unit for unit, patients started on, or switched to, Toujeo required a higher dose than patients controlled with Lantus. When switching from another basal insulin to Toujeo, patients experienced higher average fasting plasma glucose levels in the first few weeks of therapy until titrated to their individualized fasting plasma glucose targets. Higher doses were required in titrate-to-target studies to achieve glucose control similar to Lantus.
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction in patients treated with Toujeo and may be life-threatening. The long-acting effect of Toujeo may delay recovery from hypoglycemia compared to shorter-acting insulins.
Medication errors that may lead to hypoglycemia, such as accidental mix-ups between insulin products, have been reported. Patients should be instructed to always verify the insulin label before each injection.
Do not dilute or mix Toujeo with any other insulin or solution. If mixed or diluted, the solution may become cloudy, and the onset of action/time to peak effect may be altered in an unpredictable manner. Do not administer Toujeo via an insulin pump or intravenously because severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur. Discontinue Toujeo, monitor, and treat if indicated.
A reduction in the Toujeo dose may be required in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
All insulins, including Toujeo, can lead to life-threatening hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Closely monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Fluid retention, which may lead to or exacerbate heart failure, can occur with concomitant use of thiazolidinediones (TZDs) with insulin. These patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure occurs, dosage reduction or discontinuation of TZD must be considered.
Drug Interactions
Certain drugs may affect glucose metabolism, requiring insulin dosage adjustment and close monitoring of blood glucose. The signs of hypoglycemia may be reduced in patients taking anti-adrenergic drugs (e.g., beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine).
Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions commonly associated with Toujeo include hypoglycemia, hypersensitivity reactions, injection site reactions, lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash, edema, and weight gain.
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar
Toujeo SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar are single-patient-use prefilled insulin pens. To help ensure an accurate dose each time, patients should follow all steps in the Instruction Leaflet accompanying their pen; otherwise, they may not get the correct amount of insulin, which may affect their blood glucose levels. It is especially important to perform a safety test when a patient is using a new pen for the first time.
Do not withdraw Toujeo from the SoloStar and Max SoloStar single-patient-use prefilled pens with a syringe.
Click here for full Prescribing Information.
Click here for information on Sharps Medical Waste Disposal.
Click here to learn more about Sanofi's commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
FPG, fasting plasma glucose; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
‡OHIO HCPs: Prescription drug samples may only be provided to a prescriber whose practice is licensed as a Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs ("TDDD") or qualifies as exempt under Ohio law. For more information on the State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy Prescriber licensure requirements, how to obtain a TDDD license, and reasons for exemptions, please go to: http://www.pharmacy.ohio.gov/Licensing/TDDD.aspx
References:
1. Toujeo Prescribing Information. 2. Becker RHA, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):637-643. doi:10.2337/dc14-0006 3. Becker RHA, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(3):261-267. doi:10.1111/dom.12416 4. Home PD, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(12):2217-2225. doi:10.2337/dc15-0249
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection
Important Safety Information
Contraindications
Toujeo is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to insulin glargine or any of the excipients in Toujeo.
Warnings and Precautions
Toujeo contains the same active ingredient, insulin glargine, as Lantus. The concentration of insulin glargine in Toujeo is 300 units per mL (U-300).
Insulin pens and needles must never be shared between patients. Do NOT reuse needles.
Monitor blood glucose in all patients treated with insulin. Modify insulin regimens only under medical supervision. Changes in insulin regimen, strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration may result in the need for a change in insulin dose or an adjustment in concomitant oral antidiabetic treatment. Changes in insulin regimen may result in hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Dosage adjustments are recommended to lower the risk of hypoglycemia when switching patients to Toujeo from another insulin therapy.
Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis may result in hyperglycemia; sudden change in the injection site (to unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia. Advise patients to rotate injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia.
Unit for unit, patients started on, or switched to, Toujeo required a higher dose than patients controlled with Lantus. When switching from another basal insulin to Toujeo, patients experienced higher average fasting plasma glucose levels in the first few weeks of therapy until titrated to their individualized fasting plasma glucose targets. Higher doses were required in titrate-to-target studies to achieve glucose control similar to Lantus.
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction in patients treated with Toujeo and may be life-threatening. The long-acting effect of Toujeo may delay recovery from hypoglycemia compared to shorter-acting insulins.
Medication errors that may lead to hypoglycemia, such as accidental mix-ups between insulin products, have been reported. Patients should be instructed to always verify the insulin label before each injection.
Do not dilute or mix Toujeo with any other insulin or solution. If mixed or diluted, the solution may become cloudy, and the onset of action/time to peak effect may be altered in an unpredictable manner. Do not administer Toujeo via an insulin pump or intravenously because severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur. Discontinue Toujeo, monitor, and treat if indicated.
A reduction in the Toujeo dose may be required in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
All insulins, including Toujeo, can lead to life-threatening hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Closely monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Fluid retention, which may lead to or exacerbate heart failure, can occur with concomitant use of thiazolidinediones (TZDs) with insulin. These patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure occurs, dosage reduction or discontinuation of TZD must be considered.
Drug Interactions
Certain drugs may affect glucose metabolism, requiring insulin dosage adjustment and close monitoring of blood glucose. The signs of hypoglycemia may be reduced in patients taking anti-adrenergic drugs (e.g., beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine).
Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions commonly associated with Toujeo include hypoglycemia, hypersensitivity reactions, injection site reactions, lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash, edema, and weight gain.
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar
Important Safety Information for Toujeo U-300 (insulin glargine) injection SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar
Toujeo SoloStar and Toujeo Max SoloStar are single-patient-use prefilled insulin pens. To help ensure an accurate dose each time, patients should follow all steps in the Instruction Leaflet accompanying their pen; otherwise, they may not get the correct amount of insulin, which may affect their blood glucose levels. It is especially important to perform a safety test when a patient is using a new pen for the first time.
Do not withdraw Toujeo from the SoloStar and Max SoloStar single-patient-use prefilled pens with a syringe.
Click here for full Prescribing Information.
Click here for information on Sharps Medical Waste Disposal.
Click here to learn more about Sanofi's commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
FPG, fasting plasma glucose; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
‡OHIO HCPs: Prescription drug samples may only be provided to a prescriber whose practice is licensed as a Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs ("TDDD") or qualifies as exempt under Ohio law. For more information on the State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy Prescriber licensure requirements, how to obtain a TDDD license, and reasons for exemptions, please go to: http://www.pharmacy.ohio.gov/Licensing/TDDD.aspx
References:
1. Toujeo Prescribing Information. 2. Becker RHA, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):637-643. doi:10.2337/dc14-0006 3. Becker RHA, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(3):261-267. doi:10.1111/dom.12416 4. Home PD, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(12):2217-2225. doi:10.2337/dc15-0249